Problem Domain, Objects, and the DOM.
JavaScript Object Literal:

A JavaScript object literal is a comma-separated list of name-value pairs wrapped in curly braces.
Objects are variables . But objects can contain many values.
Example
var myObject = {
sProp: 'some string value',
numProp: 2,
bProp: false
};
The values are written as name:value pairs (name and value separated by a colon).
JavaScript objects are containers for named values called properties or methods.
DOM
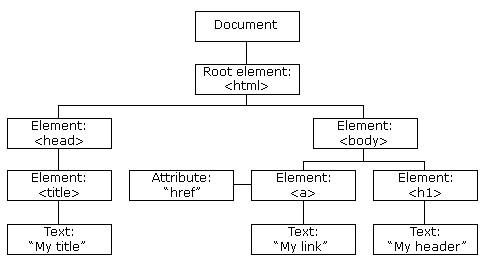
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page.
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a cross-platform and language-independent interface that treats an XML or HTML document as a tree structure wherein each node is an object representing a part of the document. The DOM represents a document with a logical tree.
The DOM is a W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) standard.
The DOM defines a standard for accessing documents:
“The W3C Document Object Model (DOM) is a platform and language-neutral interface that allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the content, structure, and style of a document.”
The W3C DOM standard is separated into 3 different parts:
-
Core DOM - standard model for all document types
-
XML DOM - standard model for XML documents
-
XML DOM - standard model for XML documents