GraphQL @connection
What is Serverless Architecture? What are its Pros and Cons?
What is Serverless Architecture?
Serverless Architecture is a software design pattern where applications are hosted by a third-party service.
What is the different between Serverless Architecture and Traditional?
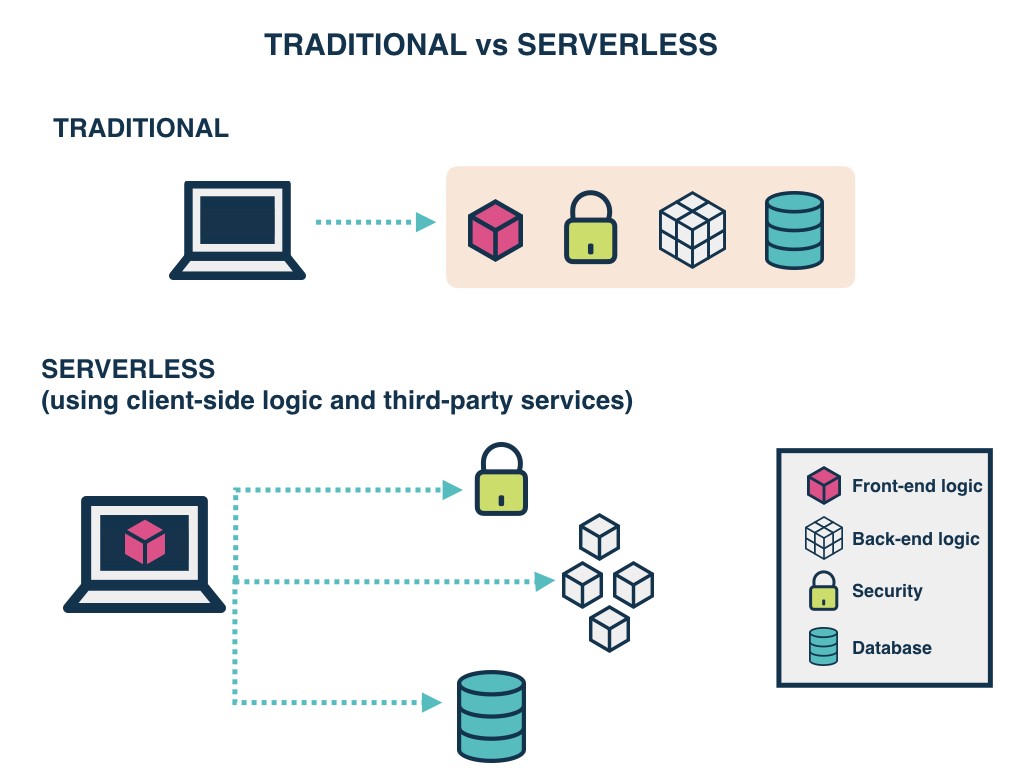
What is the different between Serverless Architecture and Traditional?

Why to use Serverless Architecture?
It is using in small projects with no need to add a big amount of dependents, also to avoid modern complex infrastructure and For saving money.
What is AWS Amplify?
Tools and services that can be used to help front-end web and mobile developers build full stack applications, powered by AWS, Without app backends.
What is GraphQL?
It is tool helps on create backends for your web and mobile applications on AWS.
Example:
type Blog @model {
id: ID!
name: String!
posts: [Post] @connection(name: "BlogPosts")
}
type Post @model {
id: ID!
title: String!
blog: Blog @connection(name: "BlogPosts")
comments: [Comment] @connection(name: "PostComments")
}
type Comment @model {
id: ID!
content: String
post: Post @connection(name: "PostComments")
}
Add relationships between types
Why to use @connection?
For making relationships between @model types.
Example:
directive @connection(keyName: String, fields: [String!]) on FIELD_DEFINITION
Has one => One to One Relation Example:
type Project @model {
id: ID!
name: String
team: Team @connection
}
type Team @model {
id: ID!
name: String!
}
Has many => Many One Relation Example:
type Post @model {
id: ID!
title: String!
comments: [Comment] @connection(keyName: "byPost", fields: ["id"])
}
type Comment @model
@key(name: "byPost", fields: ["postID", "content"]) {
id: ID!
postID: ID!
content: String!
}
Why to use Belongs to?
Add many-to-one relation to types that already have a one-to-many relation
Example:
type Post @model {
id: ID!
title: String!
comments: [Comment] @connection(keyName: "byPost", fields: ["id"])
}
type Comment @model
@key(name: "byPost", fields: ["postID", "content"]) {
id: ID!
postID: ID!
content: String!
post: Post @connection(fields: ["postID"])
}
Many-to-many relation example:
type Post @model {
id: ID!
title: String!
editors: [PostEditor] @connection(keyName: "byPost", fields: ["id"])
}
# Create a join model and disable queries as you don't need them
# and can query through Post.editors and User.posts
type PostEditor
@model(queries: null)
@key(name: "byPost", fields: ["postID", "editorID"])
@key(name: "byEditor", fields: ["editorID", "postID"]) {
id: ID!
postID: ID!
editorID: ID!
post: Post! @connection(fields: ["postID"])
editor: User! @connection(fields: ["editorID"])
}
type User @model {
id: ID!
username: String!
posts: [PostEditor] @connection(keyName: "byEditor", fields: ["id"])
}