Spring Authentication

Authentication => who are you?
Authorization or access control => what are you allowed to do?
AuthenticationManager is main interface for Authorization.
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}
An AuthenticationManager can do one of 3 things in its authenticate() method:
-
Return an Authentication (normally with authenticated=true) if it can verify that the input represents a valid principal.
-
Throw an AuthenticationException if it believes that the input represents an invalid principal.
-
Return null if it cannot decide.
Authorization or Access Control:
There are three implementations provided by the framework and all three delegate to a chain of AccessDecisionVoter instances, a bit like the ProviderManager delegates to AuthenticationProviders.
Web Security:
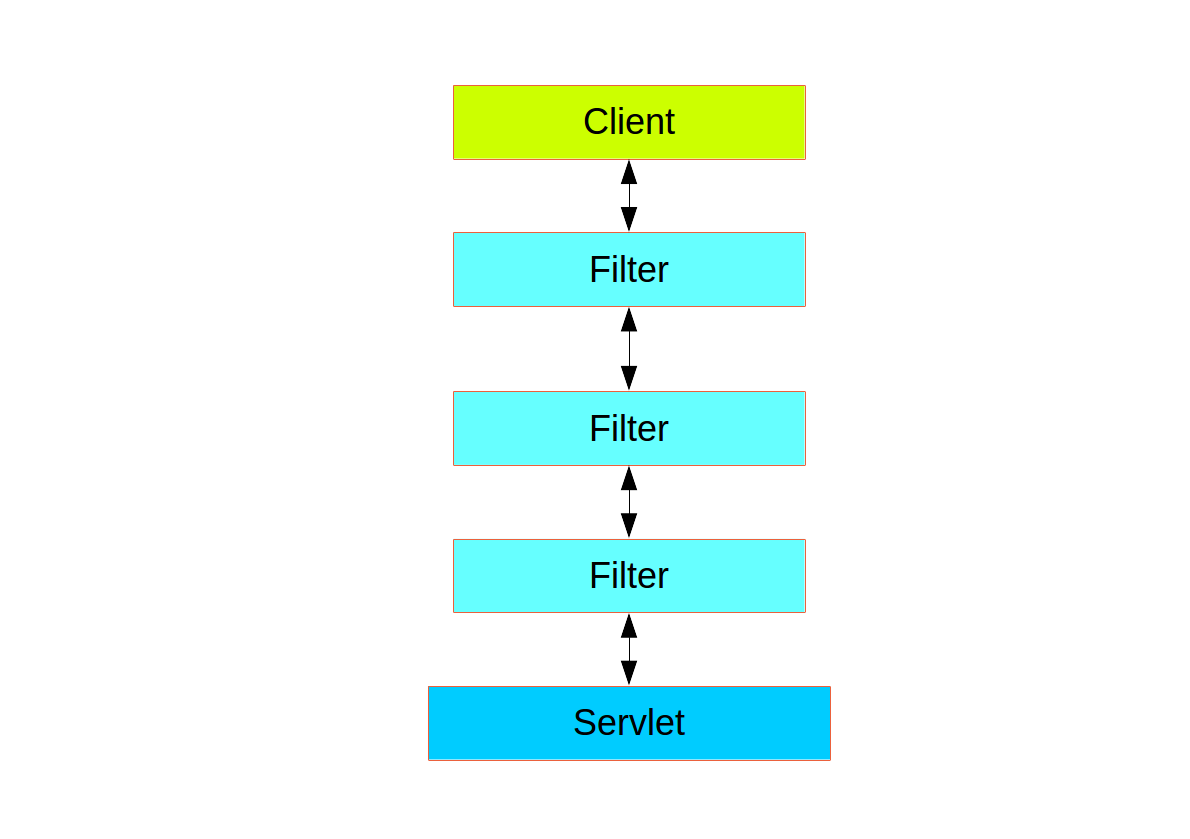
Method Security:
As well as support for securing web applications, Spring Security offers support for applying access rules to Java method executions. For Spring Security, this is just a different type of “protected resource”. For users, it means the access rules are declared using the same format of ConfigAttribute strings (for example, roles or expressions) but in a different place in your code. The first step is to enable method security — for example, in the top level configuration for our application:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class SampleSecureApplication {
}